Ing Words to Describe Cellular Respiration
THREE STAGES OF CELLULAR RESPIRATION 1. Any of various energy-yielding oxidative reactions in living matter that typically involve transfer of oxygen and production of carbon dioxide and water as end products Cellular respiration is a series of reactions occurring under aerobic conditions during which large amounts of ATP are produced.

Treasure Island Lesson Plan Lesson Planet Lesson Planet Teacher Lessons Lesson
Cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert fuel into energy and nutrients.

. Plants make their own food by photosynthesis. This energy is called adenosine triphosphate or ATP. The reason we need to breathe is to provide the oxygen needed to carry out cellular respiration in our cells.
If aerobic respiration produces 36 mol of ATP per mol of glucose what of the energy stored in glucose is a cell getting from the glucose it consumes. Glycolysis is an anaerobic process while the other two pathways are aerobic. Glycolysis the citric acid cycle and the electron transport chain.
Series of metabolic reactions that breaks down glucose into pyruvate and produces ATP. 1 mol of glucose contains 2870 kJ of chemical energy. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis pyruvate oxidation the citric acid or Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation.
There is a direct correlation between cellular respiration and exercise intensity. On the other hand photosynthesis is a process when plants produce their food from sunlight and taking carbon dioxide in and releases oxygen. The cell also must generate a number of intermediate compounds that are used in the anabolism and catabolism of macromolecules.
In order to move from glycolysis to the citric acid cycle pyruvate molecules the output of glycolysis must be oxidized in a process called pyruvate oxidation. Citric acid is broken down one carbon at a time and arranged to for the original oxaloacetic acid molecule. The process of making food glucose from inorganic molecules sun and water.
Pyruvate oxidation glycolysis the citric acid cycle and the electron transport chain. Three-carbon end product of glycolysis and starting material that is converted into acetyl CoA that enters the. Learn about cellular respiration.
Cellular Respiration can be summarized as Glucose Oxygen Carbon Dioxide Water ATP Energy Cellular Respiration in Plants But in plants cellular respiration is slightly different. Celled the power house of the cell. In order for an animals body to convert its food to energy through cellular respiration oxygen is needed.
The step of cellular respiration in which oxaloacetic acid is combined with Acetyl Co-A to form citric acid. Cellular respiration must be regulated in order to provide balanced amounts of energy in the form of ATP. Production of ATP from glucose oxidation via glycolysis the Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation.
Glycolysis is the first pathway in cellular. Discover the key ingredients in cellular respiration such as carbon dioxide and energy. An organelle that is used to produce ATP.
Hendikeps2 and 1604 more users found this answer helpful. O 2 is not required net yield of 2 ATP per glucose molecule. 30 kJ of energy is released when 1 mol of ATP is broken down into ADP.
To create ATP and other forms of energy that they can use to power their life functions cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of turning energy from that fuel into a useable form. Cellular respiration provides energy to body cells through a process of sugar burning. Electron carrier that provides high-energy electrons for photosynthesis.
Cellular respiration is a chemical reaction plants need to get energy from glucose. Finally explore the steps of cellular respiration known as glycolysis. Here through a simple process called photosynthesis plants use sunlight to turn carbon dioxide and water into glucose.
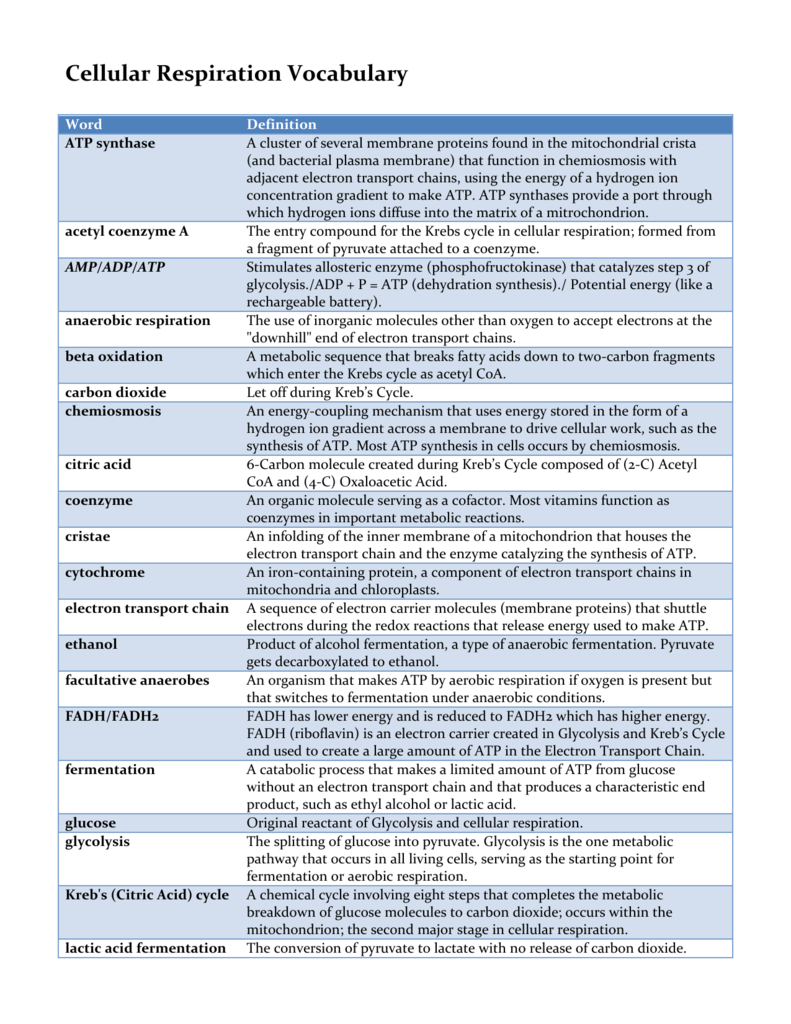
Cellular respiration is a process wherein it takes oxygen in and in return its product is carbon dioxide. Definition of cellular respiration. This vocabulary list provides relevant terms and definitions to help students understand Cellular Respiration in a college level Introduction to Biology course.
Sequence of electron carrier molecules that transfer electrons and release energy during cellular respiration. The process by which carbon dioxide is incorporated into organic compounds. Cellular respiration includes the reactions in the cells of your body when they convert the food you eat into a molecule of energy in a form your cells can use.
Cellular respiration is a process in which cells take apart food molecules and use their atoms as a source of energy. Cellular respiration uses glucose and oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water. Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP.
Breath as needed in physical exertion speech etc. 27 rows Cellular respiration aerobic respiration A process that uses food glucose and oxygen to make energy in the mitochondria. Cellular respiration is a collection of three unique metabolic pathways.
Answer a is correct. Without controls metabolic reactions would quickly come to a stand still as the forward and backward reactions. Cellular respiration Place the correct word into each sentence to describe cellular respiration ADP Cellular respiration is the process by which cells obtain by breaking down nutrients lipids glucose proteins and This breakdown is accomplished by intake of release of carbon dioxide mitochondria Cellular respiration involves the complete breakdown.
Photosynthesis involves the use of energy from sunlight water and carbon dioxide to produce glucose and oxygen. Describe the Krebs Cycle as the stepwise oxidation of pyruvate. The relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration is such that the products of one system are the reactants of the other.
3 molecules of NADH one molecule of FADH2 and one molecule of ATP are made and CO2 is released. Cellular respiration is made up of three pathways and the process known as pyruvate oxidation. 18-2 a ten-step process that occurs in the cytoplasm converts each molecule of glucose to two molecules of pyruvic acid a 3-carbon molecule an anaerobic process - proceeds whether or not O 2 is present.
Respiration uses glucose and oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water and release energy.

Free Visual Tool To Illustrate Levels Of Organization Also Serves As A Handy Little Note Organizer Levelsof Teaching Biology Biology Classroom Science Notes

Comments
Post a Comment